AI refers to systems capable of performing tasks that traditionally require humanl intelligence, such as decision-making and pattern recognition. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, leverages algorithms to learn from data and enhance performance over time. Together, they are being deployed in IT for automating tasks, enhancing cybersecurity, and managing infrastructure effectively.
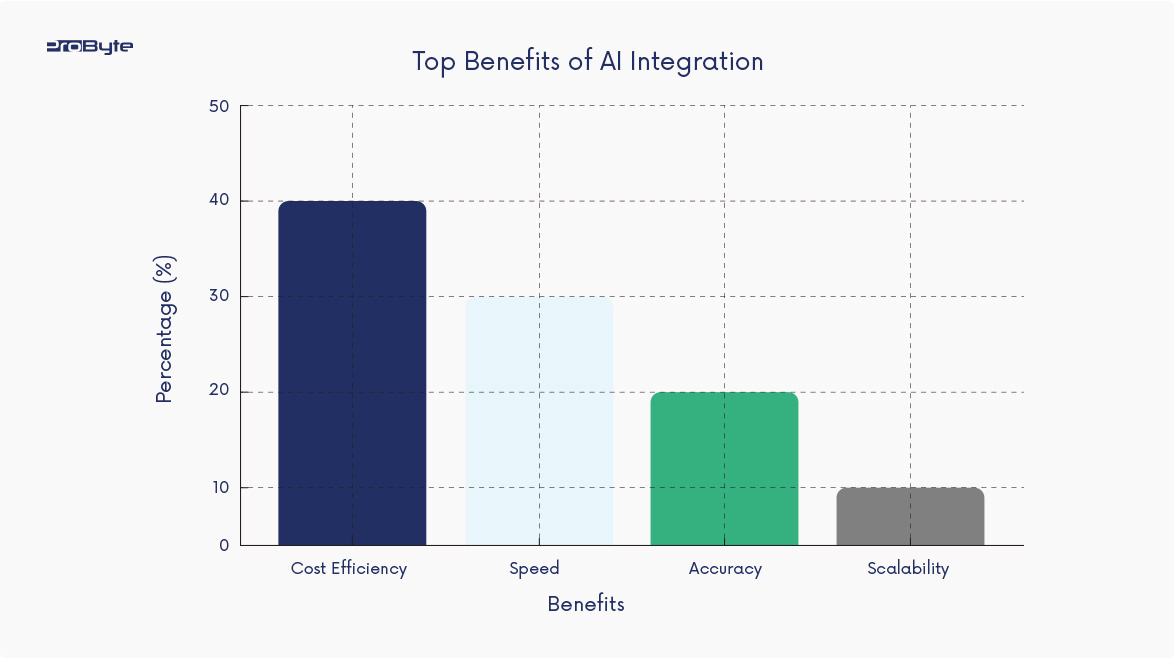
 Applications in IT Optimization
Applications in IT Optimization
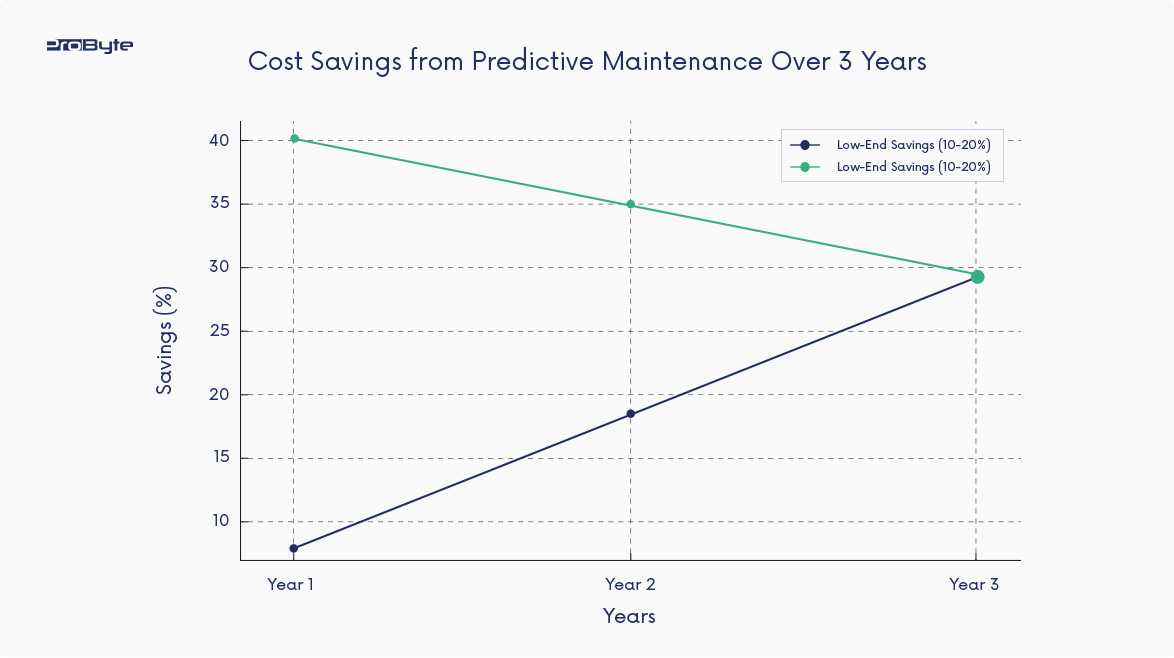
AI-powered predictive maintenance tools analyze historical data to anticipate hardware failures. For instance, manufacturing firms use AI to reduce downtime by predicting machine malfunctions before they occur, saving billions annually in operational costs
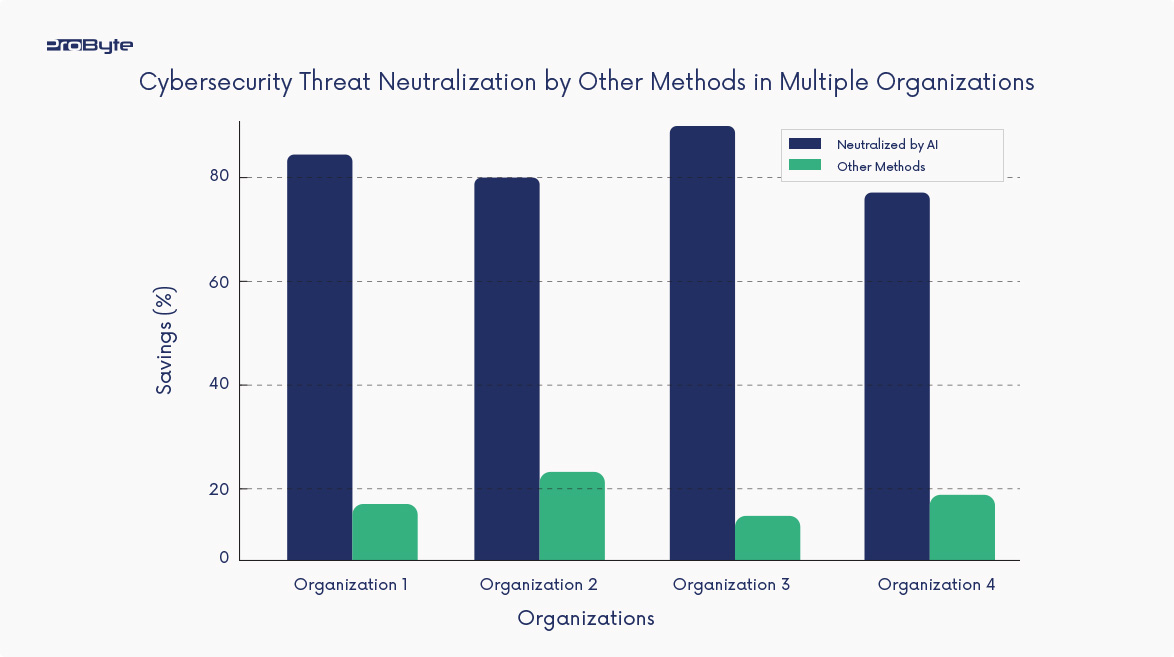
Machine Learning models can detect and neutralize threats in real time. Companies like CrowdStrike use AI to identify malware patterns, protecting networks with high efficiency. According to a study by Capgemini, 69% of organizations believe AI significantly strengthens their cybersecurity measures
Cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) use AI for dynamic resource allocation. AI algorithms predict usage spikes and automatically allocate resources, ensuring optimal performance while minimizing costs
AI chatbots and virtual assistants are revolutionizing IT support by resolving queries without human intervention. IBM Watson's AI Assistant, for example, provides customer support, reducing ticket resolution times by 30%
AI and ML optimize resource allocation, reducing costs associated with over-provisioning and operational inefficiencies. For instance, Google reported a 40% reduction in energy consumption for its data centers through AI-driven cooling systems
AI systems analyze vast datasets, offering actionable insights for IT decision-makers. Gartner projects that AI-driven decision-making tools will be used by over 75% of IT teams by 2026, improving productivity significantly
AI enables businesses to scale their operations dynamically. Machine Learning models continuously learn and adapt, ensuring seamless scalability in cloud-based environments.
Despite its potential, integrating AI in IT processes comes with challenges:
Managing sensitive data securely while training AI models is a significant concern.
There is a global shortage of professionals skilled in AI and ML
Evolving laws around AI use and accountability add complexity to deployment.
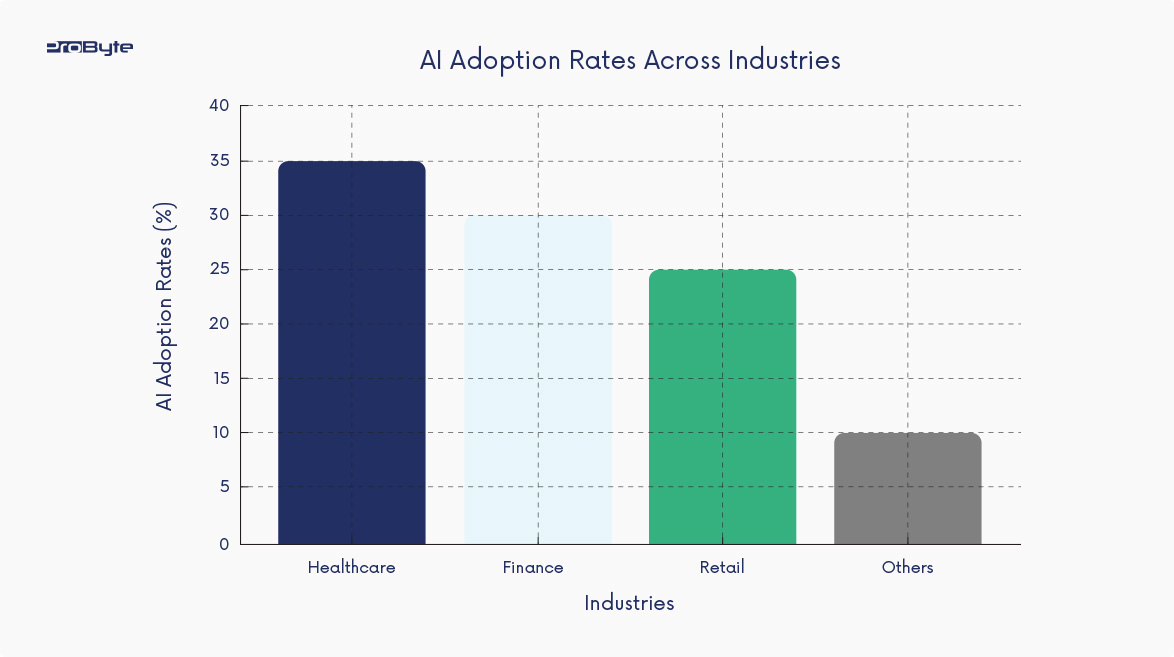
AI in healthcare IT optimizes scheduling, reduces redundant tasks, and predicts patient needs. Massachusetts General Hospital employs AI for triage, cutting patient wait times by 25%
Banks like JPMorgan Chase use ML to analyze transactional data, identifying fraudulent activities and improving customer experiences through personalized services
Walmart uses AI to predict stock levels, ensuring optimal inventory management. The system learns from sales data and adjusts procurement processes dynamically.
As AI technologies advance, the integration into IT systems will deepen. Emerging trends include:
Running AI models closer to data sources for real-time analytics.
Making AI decisions more transparent to users.
Automating deployment pipelines to improve software delivery speed.